This Blog explores practical biomedical engineering career alternatives that align with how the healthcare and life sciences industry operates today. For many biomedical engineers, career realities differ from expectations set during their academic years. While the degree prepares graduates for innovation. While the degree builds strong foundations in innovation and medical technology, the availability of core roles remains limited across regions. This gap has led many graduates to actively explore alternative careers for biomedical engineers that better align with current industry demand.
Even professionals working in core biomedical roles often experience slow growth, limited specialization, and reduced exposure to high-value areas. At the same time, the healthcare ecosystem is evolving rapidly, driven by digital platforms, data-intensive clinical systems, AI-enabled diagnostics, cloud infrastructure, and stricter regulations. As a result, choosing an alternative career for biomedical engineers has become a practical and sometimes necessary step to remain relevant and future ready.
A 2021 BME Career Exploration study highlights this shift, showing that many graduates now transition into regulated, data-driven, and technology-enabled healthcare roles. These alternative career paths for biomedical engineers leverage core strengths such as systems thinking, analytical ability, and biological understanding, offering clearer growth pathways and long-term career stability. As a result, many graduates now actively consider non-core jobs for biomedical engineers that offer clearer growth, stability, and industry alignment.
The sections below outline how each alternative career for biomedical engineers aligns with current healthcare industry needs, skill requirements, and long-term growth potential. Understanding how different roles evolve over time helps biomedical graduates evaluate long-term biomedical engineers’ career paths beyond traditional assumptions.
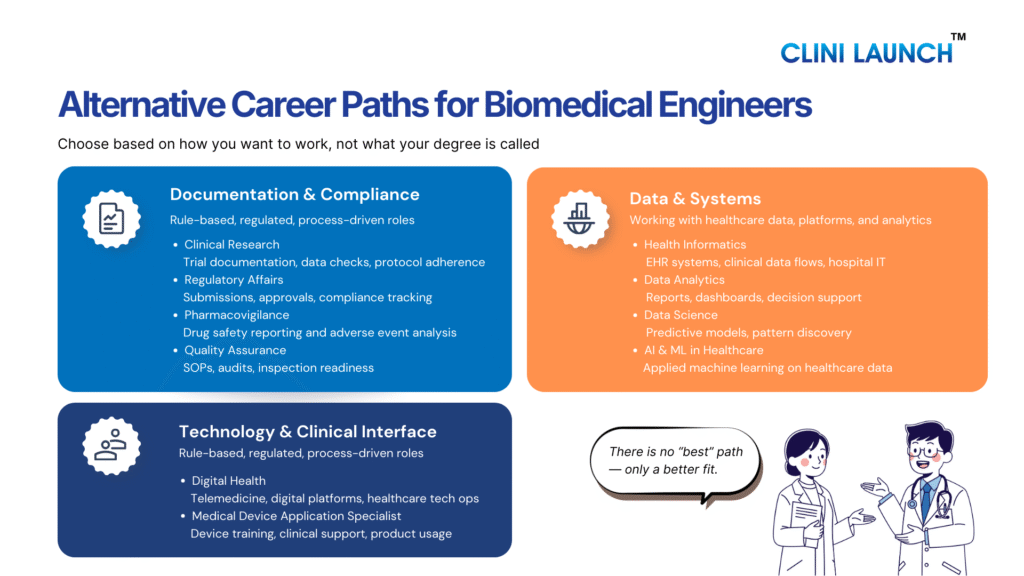
Alternative careers for biomedical engineers
The following sections outline structured healthcare careers for biomedical engineers that leverage medical knowledge, regulatory awareness, and system-based thinking.
1. Clinical Research roles
Below are some of the most practical and industry-relevant who want to work beyond traditional core engineering roles while staying connected to healthcare.
Entry-Level Roles You Can Target
- Clinical Data Coordinator
- Clinical Data Associate
- Clinical Trial Assistant (CTA)
- Clinical Research Coordinator (CRC)
- Pharmacovigilance Associate / Drug Safety Associate
- Regulatory Affairs Assistant / Junior Regulatory Associate
- Clinical Operations Executive / Trial Operations Associate
- Medical Writing Associate (Junior / Trainee)
- EDC / Clinical Systems Support Associate
These clinical research roles for biomedical engineers focus on trial execution, data integrity, and regulatory compliance across global studies.
Clinical research focuses on executing and managing clinical trials that test the safety and effectiveness of drugs, devices, and therapies. The work is centered around patient data, documentation, timelines, and regulatory compliance. These roles ensure trials are conducted strictly as per protocol so that results are acceptable to regulators. This is structured, process-driven execution, not discovery research or analytics.
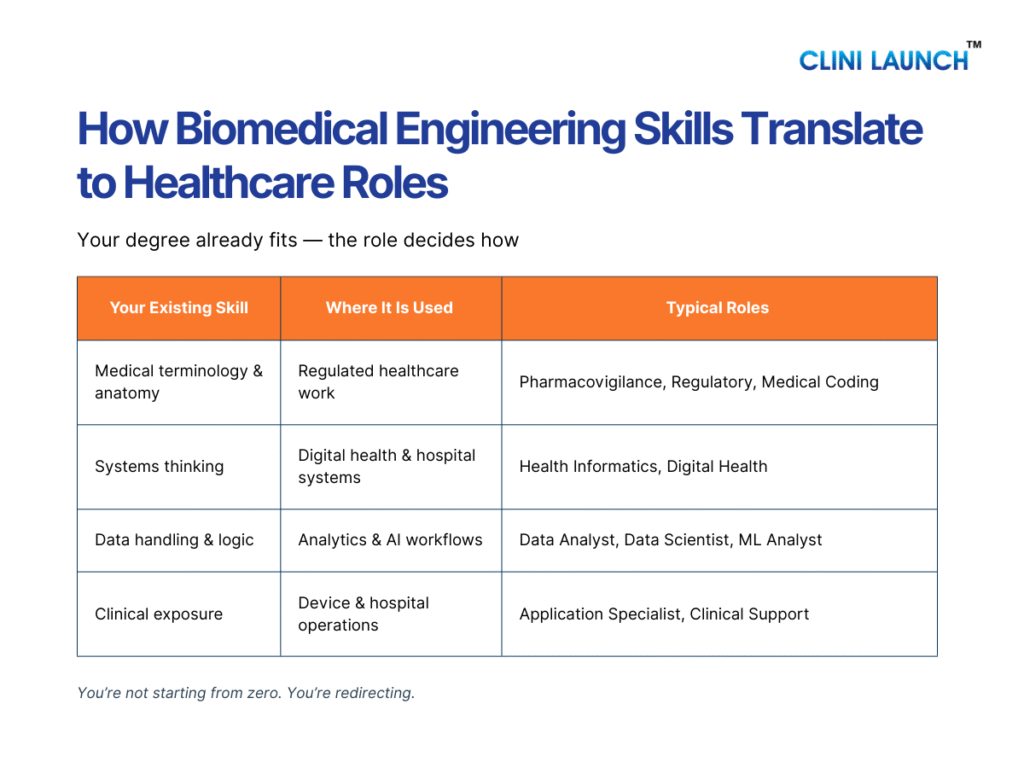
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into clinical research because they are comfortable with structured data, medical terminology, and regulated workflows. The roles reward consistency, attention to detail, and protocol adherence rather than innovation or design. For BMEs who want to stay close to healthcare systems and real-world clinical impact, this is a practical and stable career path.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
Entry-level role → Senior Associate / Analyst → Manager (role-specific)
Growth depends on trial exposure, process mastery, and regulatory experience.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level clinical research roles start between ₹2.5–4.5 LPA, depending on role, organization, and city. CROs generally offer more consistent compensation than hospital-based roles.
Companies you can apply to:
- CROs: IQVIA, Parexel, ICON, Syneos Health
- Pharma / Biotech: Pfizer, Novartis, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories
- Hospitals and academic research centers conducting sponsored trials
Outlook:
Clinical research remains stable as regulatory trials continue irrespective of market cycles. With trials becoming more global and data-intensive, the demand for compliant, well-documented execution continues to rise.
How to Get Started
Start by identifying one entry-level role and aligning your preparation toward it rather than applying broadly. Build a clear understanding of the clinical trial lifecycle, GCP principles, and role-specific workflows. For candidates without industry exposure, a structured program like Advance Diploma in Clinical Research helps bridge the gap by providing domain context, practical workflows, and hiring alignment. If internships or site-level opportunities are accessible, they should be pursued alongside or immediately after training. Networking with professionals already working in CROs or trial sites helps clarify expectations early and avoid misaligned roles.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | Clinical Research |
| Core Focus | Trial execution, data integrity, documentation, compliance |
| Entry-Level Roles | CDM, CTA, CRC, PV, Regulatory, Clinical Ops, Medical Writing |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹2.5–4.5 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | CROs, Pharma, Biotech, Hospitals |
| Key Skills Needed | GCP basics, process discipline, clinical context |
| Career Growth | Associate → Analyst → Manager |
| Long-Term Outlook | Stable, compliance-driven, globally relevant |
Clinical Research
Develop industry-ready clinical research skills used across pharmaceutical companies, CROs, and healthcare organizations. Learn how clinical trials are designed, conducted, monitored, and regulated, while gaining hands-on exposure to real-world clinical research workflows and compliance standards.

Duration: 6 months
Skills you’ll build:
Other Courses
- Clinical SAS
- Medical Coding
- Biostatistics
2.Medical Coding roles
Entry-Level Roles You Can Target
- Medical Coder (ICD-10 / CPT – Trainee / Junior)
- Certified Professional Coder (CPC – Entry Level)
- Medical Coding Analyst (Junior)
- Healthcare Documentation Specialist
- Medical Billing & Coding Associate
- Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) Associate
Medical coding jobs for biomedical engineers offer a structured, documentation-driven path within healthcare operations. Documentation-driven and compliance-focused roles represent some of the most accessible biomedical engineering jobs outside core engineering functions.
Medical coding focuses on translating clinical documentation such as physician notes, discharge summaries, diagnostic reports, and procedure records into standardized medical codes used for billing, reimbursement, audits, and compliance. The work is documentation-heavy, rule-based, and governed by strict coding guidelines and payer regulations. Accuracy and consistency are critical, as coding errors directly affect revenue, audits, and legal compliance. This is operational healthcare work, not clinical decision-making or biomedical research.
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into medical coding because they already understand medical terminology, human anatomy, disease processes, and clinical workflows. The role rewards attention to detail, structured interpretation of medical records, and adherence to classification standards rather than engineering design or innovation. For BMEs who prefer stable, desk-based healthcare roles with clear rules and measurable output, medical coding offers a predictable and scalable career path.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
Junior Medical Coder → Senior Coder / Coding Analyst → Auditor / Team Lead → Coding Manager / Compliance Specialist.
Growth depends on coding accuracy, certification upgrades, specialty exposure (e.g., inpatient, surgical, risk adjustment), and audit experience.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level medical coding roles start between ₹2.0–4.0 LPA, depending on certification status, organization, and city. Certified coders generally progress faster than non-certified entrants.
Companies you can apply to:
- Healthcare BPOs / RCM firms: Optum, CorroHealth, Omega Healthcare, Access Healthcare
- Hospitals and hospital networks
- Health insurance and payer organizations
- Medical auditing and compliance firms
Outlook:
Medical coding remains stable due to the ongoing need for standardized billing, insurance processing, and regulatory audits. While automation assists in coding, human coders are still required for complex cases, audits, and compliance-driven reviews, ensuring steady demand.
How to Get Started
Start by deciding whether you want to pursue outpatient, inpatient, or specialty coding instead of treating medical coding as a single generic role. Build strong fundamentals in ICD-10-CM, CPT, and medical documentation standards, as accuracy and guideline interpretation matter more than speed at the entry level. For candidates without prior healthcare operations exposure, a structured program such as a Advanced Diploma in Medical Coding help bridge the gap by providing coding framework clarity, real-world chart interpretation practice, and alignment with hiring expectations. Entry-level production roles or internships are critical to gaining volume-based experience and improving productivity benchmarks. Networking with experienced coders and auditors helps candidates understand certification value, audit expectations, and long-term growth paths early.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | Medical Coding |
| Core Focus | Clinical documentation coding, billing accuracy, compliance |
| Entry-Level Roles | Medical Coder, Coding Analyst, RCM Associate |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹2.0–4.0 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | Healthcare BPOs, Hospitals, Payers |
| Key Skills Needed | Medical terminology, coding guidelines, accuracy |
| Career Growth | Coder → Auditor → Manager |
| Long-Term Outlook | Stable, compliance-driven, operations-focused |
Clinical Research, Cybersecurity & Cloud Technology
Build industry-ready skills in medical coding used across hospitals, healthcare providers, insurance companies, and global healthcare services. Learn to accurately convert medical diagnoses, procedures, and services into standardized codes while ensuring compliance, accuracy, and reimbursement of integrity.

Duration: 6 months
Learn at your own pace
Skills you’ll build:
Other Courses
- Clinical Research
- Clinical SAS
- Pharmacovigilance
- AI & ML in Healthcare
3. Pharmacovigilance & Drug Safety roles
Entry-Level Roles You Can Target
- Pharmacovigilance Associate / Drug Safety Associate
- Case Processing Associate
- Safety Data Associate
- Argus Safety / PV Systems Associate (Junior)
- Pharmacovigilance Executive
- Clinical Safety Coordinator
Pharmacovigilance careers for biomedical engineer’s center on safety monitoring, adverse event reporting, and regulatory compliance.
Pharmacovigilance focuses on monitoring, evaluating, and reporting the safety of drugs, vaccines, and medical products during clinical development and post-marketing use. The work involves adverse event processing, safety data review, and regulatory reporting to global health authorities. These roles ensure that safety risks are identified, documented, and communicated accurately across the product lifecycle. This is compliance-driven safety surveillance, not laboratory research or clinical decision-making.
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into pharmacovigilance because they are familiar with medical terminology, disease mechanisms, and structured documentation. The role requires careful interpretation of clinical narratives, attention to detail, and adherence to regulatory standards rather than engineering design or experimentation. For BMEs who prefer analytical, documentation-focused healthcare roles with regulatory relevance, drug safety offers a stable and well-defined career path.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
Drug Safety Associate → Senior Safety Associate → Safety Scientist / PV Lead → Safety Manager
Growth depends on case complexity exposure, regulatory knowledge, safety database experience, and therapeutic area specialization.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level pharmacovigilance roles start between ₹2.5–5.0 LPA, depending on organization, role scope, and city.
Companies you can apply to:
- CROs: IQVIA, ICON, Parexel
- Pharma / Biotech companies with in-house safety teams
- Pharmacovigilance service providers
Outlook:
Pharmacovigilance remains stable due to increasing regulatory scrutiny and global safety reporting requirements. Demand continues if drugs and vaccines remain in use worldwide.
How to Get Started
Begin by understanding core pharmacovigilance workflows such as adverse event reporting, case processing, MedDRA coding, and global regulatory requirements. Candidates should align their preparation toward specific entry-level roles rather than applying broadly. For those without prior industry exposure, a structured program like the Advanced Diploma in Clinical Research, where pharmacovigilance and drug safety are covered as a dedicated module, helps bridge the gap by providing regulatory context and practical workflow understanding. Entry-level roles in CROs or safety teams provide the exposure needed to build accuracy and long-term role clarity.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | Pharmacovigilance & Drug Safety |
| Core Focus | Safety monitoring, case processing, regulatory reporting |
| Entry-Level Roles | Drug Safety Associate, PV Executive, Case Processor |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹2.5–5.0 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | CROs, Pharmaceutical companies, PV service providers |
| Key Skills Needed | Medical terminology, documentation, compliance |
| Career Growth | Associate → Scientist → Manager |
| Long-Term Outlook | Stable, regulation-driven, globally essential |
4. Regulatory Affairs roles
Entry-Level Roles You Can Target
- Regulatory Affairs Associate / Junior Regulatory Associate
- Regulatory Documentation Executive
- Regulatory Submissions Assistant
- Regulatory Operations Associate
- Regulatory Compliance Coordinator
Regulatory affairs jobs after biomedical engineering focus on compliance, submissions, and interaction with health authorities.
Regulatory affairs focus on ensuring that drugs, medical devices, and clinical studies comply with national and international regulatory requirements. The work involves preparing, reviewing, and maintaining regulatory documents, coordinating submissions, tracking approvals, and supporting interactions with health authorities. These roles ensure products and trials meet defined regulatory standards before and after approval. This is documentation- and compliance-driven work, not laboratory research or product development.
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into regulatory affairs because they understand medical concepts, product lifecycles, and structured documentation requirements. The role rewards attention to detail, interpretation of guidelines, and consistency in regulatory communication rather than innovation or experimentation. For BMEs who prefer policy-aligned, process-oriented roles that influence product approvals and compliance, regulatory affairs offer a clear and stable career path.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
Regulatory Associate → Senior Regulatory Associate → Regulatory Manager → Regulatory Affairs Lead.
Growth depends on regulatory exposure, submission experience, product type (drug, device, biologic), and familiarity with global guidelines.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level regulatory affairs roles start between ₹3.0–5.5 LPA, depending on organization, domain, and city.
Companies you can apply to:
- Pharma & Biotech companies with regulatory teams
- CROs supporting regulatory submissions: IQVIA, Parexel
- Medical device companies
- Regulatory consulting and compliance firms
Outlook:
Regulatory affairs remain stable as approval requirements continue to expand globally. Increasing regulatory complexity across regions sustains demand for trained regulatory professionals.
How to Get Started
Start by understanding regulatory fundamentals such as submission types, approval pathways, and global guidelines governing drugs and medical devices. Candidates should prepare specific entry-level roles rather than applying broadly across regulatory functions. For those without industry exposure, a structured program like the Advanced Diploma in Clinical Research, which includes regulatory affairs as a core module, helps build regulatory context, documentation familiarity, and workflow understanding. Entry-level roles in pharma companies or CRO regulatory teams provide practical exposure to submissions and compliance processes. Early networking with regulatory professionals helps clarify specialization paths and expectations.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | Regulatory Affairs |
| Core Focus | Regulatory compliance, submissions, approvals |
| Entry-Level Roles | Regulatory Associate, Documentation Executive |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹3.0–5.5 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | Pharma, Biotech, CROs, Medical Device firms |
| Key Skills Needed | Documentation, guideline interpretation, compliance |
| Career Growth | Associate → Manager → Lead |
| Long-Term Outlook | Stable, regulation-driven, globally relevant |
5. Quality Assurance
Entry-Level Roles You Can Target
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into quality assurance because they are trained to work with structured processes, technical documentation, and regulated environments. The role values attention to detail, risk awareness, and consistency in following procedures rather than innovation or design work. For BMEs who prefer governance-oriented roles that influence compliance and operational quality across healthcare systems, QA offers a stable and well-defined career option.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
QA Associate → Senior QA Associate → QA Manager → Quality Lead / Head
Growth depends on audit exposure, regulatory knowledge, SOP management experience, and cross-functional coordination.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level quality assurance roles start between ₹3.0–5.0 LPA, depending on organization, domain, and city.
Companies you can apply to:
- CROs: IQVIA, Parexel
- Pharma & Biotech companies
- Medical device manufacturers
- Hospitals and research organizations with QA teams
Outlook:
Quality assurance remains stable as regulatory inspections; audits, and compliance requirements continue to intensify globally. Demand persists across clinical research, pharma, and healthcare operations.
How to Get Started
Begin by understanding quality fundamentals such as SOPs, GxP guidelines, deviation management, and audit processes. Candidates should align their preparation toward entry-level QA roles rather than applying broadly across departments. For those without industry exposure, a structured program like the Advanced Diploma in Clinical Research, which includes quality assurance as a core module, helps build compliance context, documentation familiarity, and workflow understanding. Entry-level roles in CROs or regulated organizations provide practical exposure to audits and quality systems. Early interaction with QA professionals helps clarify long-term specialization paths.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | Quality Assurance |
| Core Focus | Compliance, audits, SOP adherence |
| Entry-Level Roles | QA Associate, Compliance Executive |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹3.0–5.0 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | CROs, Pharma, Medical Devices, Hospitals |
| Key Skills Needed | Documentation, process discipline, GxP basics |
| Career Growth | Associate → Manager → Lead |
| Long-Term Outlook | Stable, audit-driven, globally relevant |
6.Health Informatics roles
Entry-Level Roles You Can Target
- Health Informatics Associate
- Clinical Informatics Coordinator
- Healthcare Data Analyst (Junior)
- EHR / EMR Support Analyst
- Health Information Management (HIM) Executive
- Clinical Systems Support Associate
A health informatics career path combines healthcare data, clinical systems, and technology-enabled workflows.
Health informatics focuses on managing, analyzing, and optimizing healthcare data generated from clinical systems such as electronic health records, hospital information systems, and clinical databases. The work involves data accuracy, system workflows, interoperability, reporting, and supporting clinicians and administrators in using health data effectively. These roles sit at the intersection of healthcare, IT systems, and data governance. This is systems and data coordination work, not clinical practice or biomedical research.
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into health informatics because they understand clinical workflows, medical terminology, and system-based thinking. The role requires interpreting healthcare data, working with structured systems, and supporting technology-driven care delivery rather than engineering design or experimentation. For BMEs who want to work with healthcare data and digital systems while staying close to clinical environments, health informatics offers a practical and evolving career path.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
Health Informatics Associate → Informatics Analyst → Senior Analyst / Consultant → Informatics Manager
Growth depends on system exposure, healthcare domain knowledge, data handling skills, and familiarity with clinical information systems.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level health informatics roles start between ₹3.0–5.5 LPA, depending on organization, system complexity, and city.
Companies you can apply to:
- Hospitals and healthcare networks using digital health systems
- Health IT & informatics vendors: Cerner, Epic Systems
- Healthcare analytics and consulting firms
- CROs and pharma organizations with informatics teams
Outlook:
Health informatics continues to grow as healthcare systems digitize, and data-driven care becomes standard. Demand increases with expanding EHR adoption, interoperability requirements, and healthcare analytics needs.
How to Get Started
Begin by understanding healthcare data flows, EHR concepts, clinical documentation standards, and basic health data governance. Candidates should target specific entry-level informatics or clinical systems roles rather than applying broadly across IT or analytics positions. At CliniLaunch Research Institute, relevant programs such as the PG Diploma in AI/ML in Healthcare and clinical research programs that expose learners to healthcare data systems and clinical workflows help build foundational informatics understanding. Entry-level roles in hospitals, health IT teams, or healthcare analytics firms provide practical exposure to real-world systems and data environments.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | Health Informatics |
| Core Focus | Healthcare data systems, EHRs, clinical workflows |
| Entry-Level Roles | Informatics Associate, EHR Analyst |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹3.0–5.5 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | Hospitals, Health IT firms, Analytics companies |
| Key Skills Needed | Clinical data understanding, systems thinking |
| Career Growth | Associate → Analyst → Manager |
| Long-Term Outlook | Growing, data-driven, healthcare-focused |
7. Digital Health roles
Entry-Level Roles You Can Target
- Digital Health Executive
- Health Technology Associate
- Clinical Digital Operations Associate
- Digital Health Project Coordinator
- Healthcare Technology Support Analyst
- Digital Health Data Associate (Junior)
Digital health jobs for biomedical engineers involve supporting technology platforms used in modern healthcare delivery.
Digital health focuses on the use of technology to improve healthcare delivery, patient monitoring, clinical workflows, and health data management. The work involves supporting digital platforms such as telemedicine systems, remote patient monitoring tools, clinical dashboards, and healthcare applications. These roles bridge healthcare operations and technology by ensuring digital tools are implemented, used, and maintained effectively. This is technology-enabled healthcare operations, not software development or clinical practice.
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into digital health because they understand both healthcare systems and technology-driven workflows. The role values systems thinking, clinical context awareness, and the ability to work across medical and technical teams rather than pure coding or engineering design. For BMEs who want to be part of healthcare innovation without moving into core IT development roles, digital health offers a flexible and future-facing career path.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
Digital Health Associate → Digital Health Analyst → Senior Analyst / Consultant → Digital Health Manager
Growth depends on platform exposure, healthcare domain knowledge, data handling skills, and cross-functional coordination.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level digital health roles start between ₹3.0–6.0 LPA, depending on organization, role scope, and city.
Companies you can apply to:
- Digital health and health-tech companies
- Hospitals adopting telemedicine and digital care platforms
- Healthcare analytics and technology consulting firms
- Pharma and CROs implementing digital trial solutions
Outlook:
Digital health continues to expand as healthcare systems adopt virtual care, remote monitoring, and data-driven decision-making. Demand is driven by technology adoption rather than traditional healthcare hiring cycles.
How to Get Started
Begin by understanding digital health fundamentals such as telemedicine workflows, healthcare data integration, digital clinical platforms, and patient engagement systems. Candidates should target entry-level digital health or healthcare technology coordination roles rather than generic IT positions. At CliniLaunch Research Institute, programs such as the PG Diploma in AI/ML in Healthcare and clinical research programs provide exposure to healthcare data, digital tools, and clinical workflows that are directly relevant to digital health roles. This combination helps learners understand how technology, data, and clinical operations intersect in real healthcare environments. Entry-level roles in health-tech companies or hospital digital teams provide practical exposure to digital healthcare systems.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | Digital Health |
| Core Focus | Healthcare technology, digital platforms, workflows |
| Entry-Level Roles | Digital Health Associate, Tech Support Analyst |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹3.0–6.0 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | Health-tech firms, Hospitals, Consulting companies |
| Key Skills Needed | Healthcare context, systems thinking, coordination |
| Career Growth | Associate → Analyst → Manager |
| Long-Term Outlook | Growing, technology-driven, healthcare-focused |
8. Data Analytics roles
Data Analytics roles
- Data Analyst (Junior)
- Healthcare Data Analyst
- Clinical Data Analyst (Non-statistical)
- Business / Reporting Analyst (Healthcare)
- Data Operations Associate
- Analytics Support Associate
Healthcare data analytics careers focus on turning clinical and operational data into actionable insights.
Data analytics focuses on collecting, cleaning, analyzing, and interpreting structured data to support decision-making. In healthcare and life sciences, this includes clinical data, operational metrics, patient outcomes, and business performance data. The work involves dashboards, reports, trend analysis, and data validation rather than predictive modeling or advanced research. These roles support operational and strategic decisions using existing data systems. This is applied data analysis, not core data science or algorithm development.
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into data analytics because they are comfortable working with data, structured problem-solving, and interpreting technical information within a healthcare context. The role values analytical thinking, logical reasoning, and the ability to translate data into meaningful insights rather than deep programming or mathematical research. For BMEs who want to work with data while staying connected to healthcare and life sciences, data analytics offers a flexible and transferable career option.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
Junior Data Analyst → Data Analyst → Senior Analyst → Analytics Manager / Lead
Growth depends on domain expertise, data handling skills, reporting accuracy, and exposure to real business or clinical datasets.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level data analytics roles start between ₹3.0–6.0 LPA, depending on industry, tools used, and organization.
Companies you can apply to:
- Healthcare and life sciences organizations
- Analytics and consulting firms
- Hospitals and health-tech companies
- CROs and pharma companies using data-driven operations
Outlook:
Data analytics remain in demand as organizations rely increasingly on data for operational efficiency and decision-making. In healthcare, demand continues due to growing data volumes and digital system adoption.
How to Get Started
Begin by understanding data analytics fundamentals such as data cleaning, basic statistics, reporting, and visualization. Candidates should focus on entry-level analyst roles rather than advanced data science positions. At CliniLaunch Research Institute, programs like the PG Diploma in AI/ML in Healthcare provide exposure to healthcare datasets, analytical tools, and applied use cases that are relevant to analytics roles. This foundation helps learners connect data analysis with real healthcare and clinical scenarios. Entry-level analysts or reporting roles provide the practical experience needed to grow within the analytics domain.
How to Get Started
Begin by understanding data analytics fundamentals such as data cleaning, basic statistics, reporting, and visualization. Candidates should focus on entry-level analyst roles rather than advanced data science positions. At CliniLaunch Research Institute, programs like the PG Diploma in AI/ML in Healthcare provide exposure to healthcare datasets, analytical tools, and applied use cases that are relevant to analytics roles. This foundation helps learners connect data analysis with real healthcare and clinical scenarios. Entry-level analysts or reporting roles provide the practical experience needed to grow within the analytics domain.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | Data Analytics |
| Core Focus | Data analysis, reporting, decision support |
| Entry-Level Roles | Data Analyst, Reporting Analyst |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹3.0–6.0 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | Healthcare firms, Analytics companies |
| Key Skills Needed | Data handling, analytical thinking, tools |
| Career Growth | Analyst → Senior Analyst → Manager |
| Long-Term Outlook | Stable, data-driven, cross-industry |
9. Data Science roles
Entry-Level Roles You Can Target
- Data Scientist (Junior)
- Associate Data Scientist
- Machine Learning Analyst (Entry-Level)
- Healthcare Data Scientist (Junior)
- AI/ML Analyst (Trainee)
- Applied Analytics Associate
Data science represents one of the most advanced life sciences career options for biomedical engineers with analytical strengths.
Data science focuses on using data to build predictive models, identify patterns, and support complex decision-making. In healthcare and life sciences, this includes working with clinical data, patient outcomes, operational datasets, and real-world evidence to generate insights using statistical methods and machine learning techniques. The work involves data preparation, model development, validation, and interpretation rather than routine reporting. This is applied to modeling and analytics, not pure software engineering or academic research.
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into data science because they combine analytical thinking with a strong domain understanding of healthcare and biological systems. The role benefits from problem-solving ability, comfort with data-driven reasoning, and the capacity to interpret results within a medical or clinical context. While additional skills in programming and statistics are required, BMEs often adapt well because they already understand the complexity and variability of healthcare data. For those willing to build deeper analytical expertise, data science offers high-impact roles across healthcare and life sciences.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
Junior Data Scientist → Data Scientist → Senior Data Scientist → Data Science Lead / Manager
Growth depends on model-building capability, domain expertise, problem complexity handled, and business or clinical impact of solutions.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level data science roles start between ₹4.5–8.0 LPA, depending on skill depth, industry, and organization.
Companies you can apply to:
- Healthcare and life sciences analytics firms
- Health-tech and AI-driven healthcare companies
- Pharma, biotech, and CROs using advanced analytics
- Consulting and data science service organizations
Outlook:
Data science continues to grow as healthcare organizations adopt AI-driven decision-making and predictive analytics. Demand remains strong for professionals who can combine technical modeling skills with healthcare domain understanding.
How to Get Started
Begin by building strong fundamentals in data handling, statistics, and programming before moving into machine learning concepts. Candidates should target junior or associate data science roles rather than expecting direct entry into advanced modeling positions. At CliniLaunch Research Institute, the PG Diploma in AI/ML in Healthcare provides exposure to healthcare datasets, applied machine learning workflows, and real-world use cases relevant to data science roles. This foundation helps learners connect algorithms with clinical and healthcare problems. Entry-level analytics or ML trainee roles provide the practical experience needed to progress within the data science domain.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | Data Analytics |
| Core Focus | Data analysis, reporting, decision support |
| Entry-Level Roles | Data Analyst, Reporting Analyst |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹3.0–6.0 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | Healthcare firms, Analytics companies |
| Key Skills Needed | Data handling, analytical thinking, tools |
| Career Growth | Analyst → Senior Analyst → Manager |
| Long-Term Outlook | Stable, data-driven, cross-industry |
10. AI & ML in Healthcare
Entry-Level Roles You Can Target
- AI/ML Analyst (Healthcare – Junior)
- Healthcare Machine Learning Associate
- Clinical AI Analyst
- Healthcare Data Science Associate (AI-focused)
- AI Solutions Analyst (Healthcare)
- Applied AI Analyst (Life Sciences)
AI and ML in healthcare careers apply machine learning models to clinical, imaging, and healthcare datasets.
AI and ML in healthcare focus on applying machine learning models and data-driven algorithms to healthcare, clinical, and life sciences data. The work involves developing, testing, and validating models for use cases such as disease prediction, patient risk stratification, medical imaging support, clinical decision support, and operational optimization. These roles sit at the intersection of healthcare data, analytics, and applied machine learning. This is applied to AI work, not software engineering or academic research.
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into AI and ML roles because they understand healthcare data complexity, clinical context, and biological variability. The role requires analytical thinking, problem formulation, and the ability to interpret model outputs in a medical or clinical setting rather than only focusing on algorithms. For BMEs willing to build strong foundations in data handling, statistics, and machine learning, AI and ML in healthcare offer high-impact and future-facing career opportunities.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
AI/ML Analyst → Machine Learning Engineer / Data Scientist → Senior AI Specialist → AI Lead / Manager.
Growth depends on model deployment exposure, domain-specific use cases handled, and the ability to translate AI outputs into healthcare decisions.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level AI and ML healthcare roles start between ₹5.0–9.0 LPA, depending on skill depth, tools proficiency, and organization.
Companies you can apply to:
- Health-tech and AI-driven healthcare companies Niramai Health Analytix, Qure .ai
- Pharma, biotech, and CROs using AI for trials and RWE
- Healthcare analytics and AI consulting firms
- Hospitals and research organizations adopting AI solutions
Outlook:
AI and ML adoption in healthcare continues to expand, driven by increasing data availability and demand for predictive, automated decision-support systems. Roles favor professionals who combine technical skills with healthcare domain understanding.
How to Get Started
Begin by building strong foundations in data analytics, statistics, and programming before moving into machine learning concepts and healthcare use cases. Candidates should target junior or associate AI/ML roles rather than advanced research positions initially. At CliniLaunch Research Institute, the PG Diploma in AI/ML in Healthcare provides structured exposure to healthcare datasets, applied machine learning workflows, and real-world clinical use cases. This helps learners understand how AI models are built, validated, and interpreted within healthcare environments. Entry-level analysts or AI trainee roles provide the practical experience required to progress in this domain.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | AI & ML in Healthcare |
| Core Focus | Applied machine learning, healthcare data modeling |
| Entry-Level Roles | AI/ML Analyst, Clinical AI Associate |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹5.0–9.0 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | Health-tech companies, Pharmaceutical firms, Analytics companies |
| Key Skills Needed | Machine learning fundamentals, data handling, healthcare context |
| Career Growth | Analyst → Specialist → Lead |
| Long-Term Outlook | Growing, skill-driven, high-impact |
AI & ML in Healthcare
Build future-ready skills at the intersection of artificial intelligence and healthcare. Learn how AI and machine learning are applied in clinical research, medical imaging, diagnostics, drug discovery, and healthcare data analytics to solve real-world healthcare problems.

Duration: 6 months
Skills you’ll build:
Other Courses
11. Medical Devices & Application Specialist Roles
Entry-Level Roles You Can Target
- Application Specialist (Medical Devices – Junior)
- Clinical Application Executive
- Product Support Specialist (Medical Devices)
- Field Application Associate
- Technical Clinical Support Executive
- Device Training & Support Associate
Medical device application specialist jobs combine clinical exposure with hands-on device support and training.
Medical device application roles focus on supporting the clinical use, setup, and optimization of medical devices used in hospitals and diagnostic settings. The work involves product demonstrations, user training, troubleshooting, clinical workflow support, and coordination between clinicians and device companies. These roles ensure devices are used safely, effectively, and as intended in real-world healthcare environments. This is application and clinical support work, not device design or core R&D.
Why Biomedical Engineers Fit Well
Biomedical engineers fit well into application specialist roles because they understand medical devices, clinical environments, and technology–user interaction. The role values product knowledge, communication with clinicians, and practical problem-solving rather than engineering design or laboratory research. For BMEs who prefer hands-on clinical exposure and interaction with healthcare professionals, this path offers a direct connection to patient care through technology.
Career Progression, Salary, and Companies
Career progression (typical):
Application Specialist → Senior Application Specialist → Product / Clinical Manager → Regional Product Lead
Growth depends on device expertise, clinical exposure, communication skills, and territory or product responsibility.
Average entry-level salary (India):
Most entry-level application specialist roles start between ₹3.0–6.0 LPA, depending on device category, organization, and city.
Companies you can apply to:
- Medical device manufacturers: Medtronic, Philips, GE Healthcare
- Diagnostic and imaging companies
- Medical equipment distributors and service partners
- Hospitals using advanced medical devices
Outlook:
Medical device application roles remain steady as hospitals continue adopting advanced technologies. Demand grows with the introduction of new devices that require structured clinical training and support.
How to Get Started
Begin by understanding basic medical device principles, clinical workflows, and user training requirements. Candidates should target application or clinical support roles rather than pure sales positions. At CliniLaunch Research Institute, exposure gained through the Advanced Diploma in Clinical Research helps learners understand clinical environments, regulatory expectations, and device usage within trials and healthcare settings. Entry-level roles with device companies or distributors to provide hands-on exposure to products and clinical users.
| Aspect | Details |
| Domain | Medical Devices & Applications |
| Core Focus | Device usage, clinical support, user training |
| Entry-Level Roles | Application Specialist, Clinical Support |
| Entry Salary (India) | ₹3.0–6.0 LPA (average) |
| Hiring Organizations | Medical device companies, Hospitals, Distributors |
| Key Skills Needed | Device knowledge, clinical communication |
| Career Growth | Associate → Specialist → Manager |
| Long-Term Outlook | Stable, technology-driven, clinically relevant |
Conclusion
Identifying the best careers after biomedical engineering requires clarity on industry expectations, role realities, and long-term skill relevance. For those navigating uncertainty after graduation or early in their careers, selecting an alternative career for biomedical engineers should be a structured decision based on role clarity, industry demand, and long-term relevance rather than short-term trends.
Biomedical engineers, career growth today depends less on job titles and more on how well their skills align with evolving industry needs. Healthcare organizations increasingly seek professionals who understand systems, processes, data, and regulatory expectations. This creates meaningful opportunities beyond traditional roles for those willing to adapt and upskill with clarity. Making informed career choices, understanding role expectations early, and preparing with the right foundation can help biomedical engineers build stable and relevant careers in a changing healthcare landscape.





